- Fares Laroui
- September 24, 2019
The evolution of blockchain and how it can be used by enterprises

Content
What is blockchain?
How far has the technology come in recent years?
What are the most popular use cases of blockchain by enterprises?
1. Defining blockchain
Blockchain is a public ledger that uses a chain of blocks to store different kinds of records. It has key benefits for businesses, such as decentralisation, persistency, anonymity and auditability. The technology has been used for various applications so far, from cryptocurrencies and financial services to healthcare and public services. The blockchain’s potential extends beyond its current applications, with its decentralized, persistent, and auditable nature making it an ideal foundation for metaverse development services. Additionally, the rise of rwa tokenization, which allows real-world assets to be represented as digital tokens on the blockchain, further expands the possibilities for integrating tangible assets into the digital realm.
As the blockchain ecosystem continues to evolve, innovative platforms like MaxSwap are emerging, offering decentralized solutions for seamlessly swapping cryptocurrencies while leveraging the inherent benefits of blockchain technology, such as enhanced security, transparency, and elimination of intermediaries.
2. How far has blockchain come?
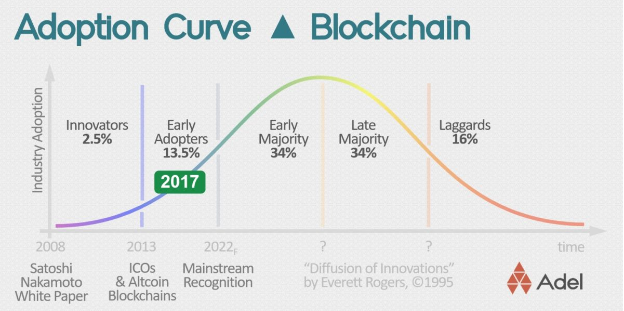
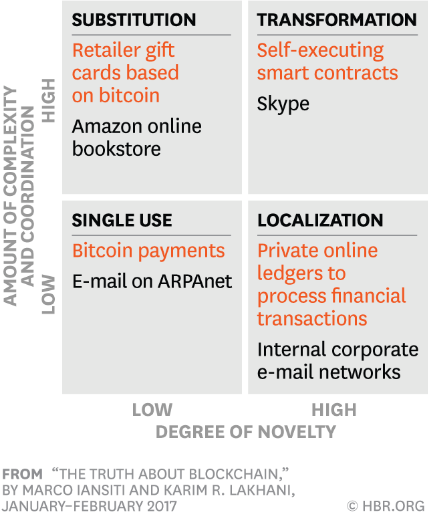
Source: https://hbr.org/2017/01/the-truth-about-blockchain#comment-section
- Single use: This stage is characterized by low novelty and complexity applications, in which the applications tend to be quite simple, less costly and designed for a sole purpose.
- Localization: Applications in this stage are high in novelty but low in complexity, with a limited number of adopters creating value and facilitating adoption.
- Substitution: Applications during the substitution stage are low in novelty since they come as a logical continuation of single-use applications, but high in complexity because they target public use.
- Transformation: The transformation stage occurs when applications have a significant impact on economic, social and political systems. The prime example of a technology that has reached this stage is the Internet.
3. Use cases of blockchain in enterprises
Knowledge sharing and record keeping
One of the main reasons why there is so much interest in blockchain is the fact that it is virtually unhackable. With the use of encryption, each user has a public key and a private key that he/she can use to validate and access different transactions and records. The enhanced security offered by blockchain technology has made tech companies consider introducing it to support knowledge sharing and record keeping. Technologies such as Web3, NFT marketplace development, and DLT platforms have begun to evolve.
Employee engagement
Human resources
A number of start-ups have emerged lately with innovative ideas targeting the HR field. These new initiatives cover the whole scope of HR operations, from recruitment to payroll management. The ability of blockchain to facilitate transactions, eliminate intermediaries and promote transparency is contributing to the growth (although not that rapid) of these solutions.
discover all the features and benefits
Related posts
- All
- eXo
- Digital workplace
- Open source
- Internal communication
- Collaboration
- News
- intranet
- Future of work
- workplace
- Knowledge management
- Employee engagement
- Employee experience
- Employee productivity
- onboarding
- Employee recognition
- Change management
- Cartoon
- Digital transformation
- Infographic
- Remote work
- Tips & Tricks
- Tutorial
- Uncategorized
Leave a Reply
( Your e-mail address will not be published)


